Image from USDA
Characteristics of Arizona Planting Region
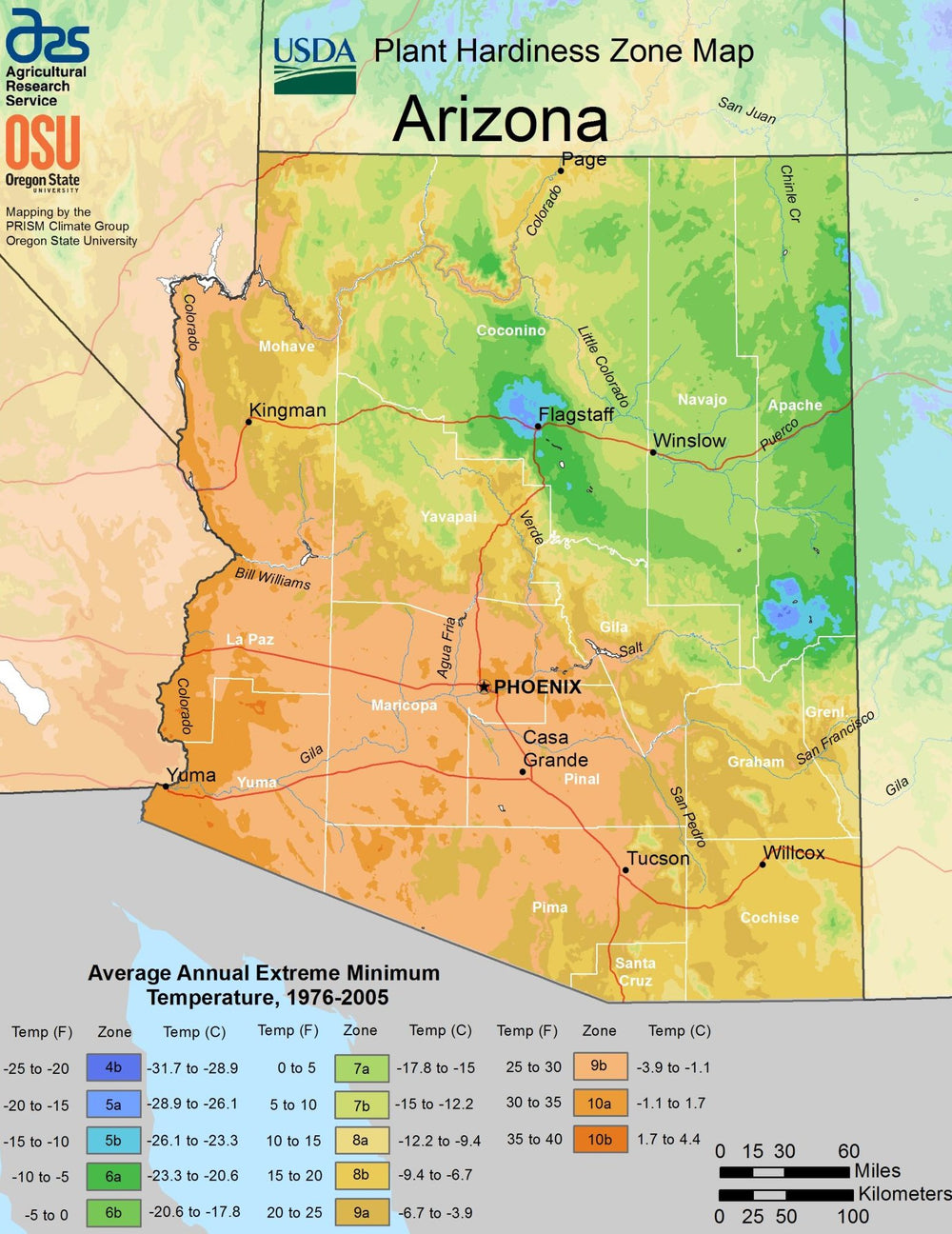
Arizona has an arid desert climate with little precipitation throughout the year, making it one of the driest states in the US. As a result, summers in southern regions are hot and dry, while winters are mild with rain. However, summers are cooler in the northern parts of the state, while winters can be harsh, with moderate snowfall.
Regardless of where you live in Arizona, you're likely to experience a variety of extreme weather situations, including:
- Extreme Heat
- Wildfires
- Long Droughts
- Monsoons
- Flash Floods
- Dust Storms
- Hail
- Tornadoes
Despite the extreme weather conditions, most of the state will experience an ideal growing timeframe from the end of January through early December, with an average of 316 frost-free days throughout the year.

1. Extreme Heat
Summers in Arizona are scorching hot, with temperatures typically ranging from 90°F (32.2°C) to 120°F (48.9°C). This extreme heat can be particularly stressful on your garden, wilting and shrivelling up young plants. A greenhouse can be used to provide a ventilated space for your plants to thrive even on the hottest days.
2. Low Humidity
Due to the dry climate, Arizona has some of the lowest humidity levels across the entire USA. Unfortunately, this can create a difficult environment for your garden to flourish. It’s recommended to use a greenhouse as a way to control humidity levels and provide a moist space for your plants to grow healthily.
3. Intense Droughts
Year after year, the entire state of Arizona is subjected to intense, prolonged droughts. To combat these gruelling growing conditions, many gardeners will utilize a greenhouse to capture moisture and maximize the limited water used in their garden.

The Benefits of Using a Greenhouse in Arizona
While many Arizonans enjoy lengthy planting seasons free of early frosts, the extreme environmental conditions present a new variety of challenges for your garden's health. Greenhouse growing can be used as an effective tool to regulate humidity, protect your plants from severe weather events, and cool them down in the sweltering summer weather.
1. Extend Your Growing Season
-
Without a Greenhouse:
Arizona’s growing season is exceptionally long; however, it can vary dramatically across the state. In southern regions, such as Phoenix, gardeners have ideal temperatures for around 260 days of growing. Alternatively, in northern, high-altitude areas such as Flagstaff, the season is significantly shorter at 103 days.
-
With a Greenhouse:
Across the state of Arizona, a greenhouse can lengthen and improve planting seasons. In cool, high-altitude places, gardeners can add an extra 2-6 months to their growing time, while residents of hotter regions can create a cool, moist environment to protect plants from severe heat.
Learn more about specific growing dates for your area and the best vegetables to plant in each part of Arizona.

Customer images of their Sungrow Greenhouse setup in a similar climate
2. Grow a Wider Variety of Vegetables
-
Without a Greenhouse:
Arizona’s dry heat, low humidity, and prolonged droughts mean that outdoor gardeners should focus on warm-season fruits and vegetables that don’t require a great deal of watering. The following plants are recommended for Arizona’s desert climate:
- Tomatoes
- Peppers
- Corn
- Chillies
- Eggplant
- Okra
- Sunflower
- Pumpkin
-
With a Greenhouse:
Greenhouse owners have a multitude of different options for what can be successfully planted in their gardens. Heat-friendly fruits, delicate herbs, and cold-loving vegetables can all grow in abundance in this space, regardless of the weather outside. Passionate gardeners will be thrilled to know that the following vegetables will thrive in a greenhouse:
- Basil
- Lettuce
- Parsley
- Cucumbers
- Broccoli
- Turnips
- Spinach
- Collard Greens
- Leeks
- Cauliflower
- Cilantro
- Kale
- Cilantro
- Onions
- Radishes
- Carrots
- Kohlrabi
- Mint
- Dill
- Chives
- Cabbage

Planting Basil
Why Planta Greenhouses?
- Wind resistant up to 65 mph (learn more about how our greenhouses hold up in high-altitude climates).
- Withstands a snow load of up to 98 psf (480kg/square meter).
- Made with a heavy-duty galvanized steel frame.
- Polycarbonate panels provide 100% protection against UV rays.
- The Sungrow greenhouse is bell-shaped - allows the wind, snow, and hail to slide off the sides.
- Extendable (Sungrow, Sigma and Farmer models can be extended beyond 100ft)
- Made in Europe and are exclusively imported
- Maintenance-free