Image from USDA
Characteristics of Iowa’s Planting Region
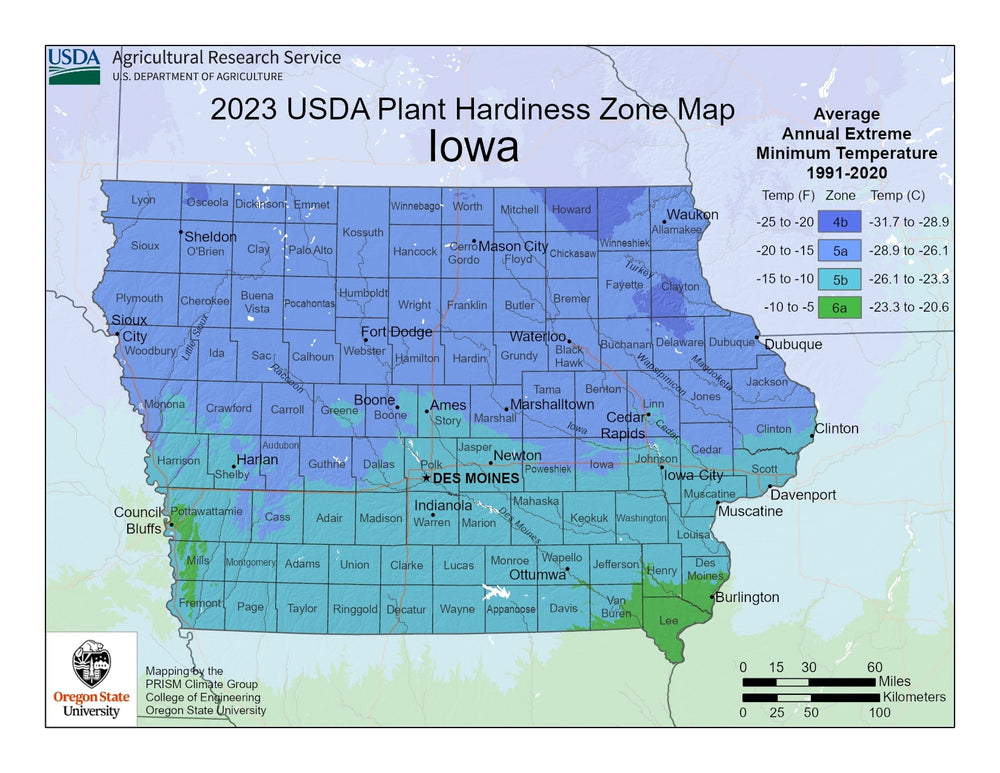
Iowa's climate is humid continental, characterized by hot summers, cold winters, and ample precipitation throughout the year.
The state's position in the heart of the Midwest, far from moderating coastal influences, leads to more extreme temperature fluctuations compared to coastal states.
As a gardener in the Hawkeye State, you can expect:
- Hot summers, with July temperatures averaging around 74°F to 76°F (23.3°C to 24.4°C)
- Cold winters, particularly in northern areas, with January averages ranging from 14°F to 22°F (-10°C to -5.6°C)
- Significant temperature variations between seasons and even within a single day
- Annual precipitation averaging 30-34 inches (76-86 cm), with slightly higher amounts in the southeast
- Occasional extreme weather events, including tornadoes, severe thunderstorms, and blizzards
Despite these varied conditions, Iowa offers a favorable growing environment for many plants, especially those well-suited to continental climates.
The state's growing season typically ranges from 150 days in the north to 180 days in the south, providing ample time for the cultivation of a wide variety of crops.

Challenges of Growing in Iowa
Temperature Fluctuations
Iowa's inland location leads to significant temperature swings, which can stress plants. Late spring frosts and early fall freezes can damage tender crops.
Soil Variability
While Iowa is famous for its rich, dark soil, soil types can vary across the state. The Loess Hills in western Iowa have wind-deposited silt soils, while parts of southern Iowa have clay-based soils that can be challenging for drainage.
Pest and Disease
The state's agricultural prominence can lead to significant pest and disease issues. Corn earworms, soybean aphids, and various fungal diseases are common challenges for Iowa gardeners and farmers.

The Benefits of Using a Greenhouse in Iowa
While Iowa's climate supports a robust agricultural sector, a greenhouse can significantly enhance your growing capabilities:
1. Extend Your Growing Season
- Without a Greenhouse: In central Iowa, outdoor planting typically begins in early May and ends in late September to early October.
- With a Greenhouse: Greenhouse gardeners can start seeds as early as late February and continue harvesting into late November or even December. This extension is particularly beneficial for warm-season crops like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers.
Learn more about your area's specific growing dates and the best vegetables to plant in each part of Georgia.

Customer images of their Greenhouse setup in Iowa
2. Grow a Wider Variety of Vegetables Without a Greenhouse:
- Without a Greenhouse
Iowa's outdoor conditions are ideal for crops like:
|
|
- With a Greenhouse
You can create microclimates suitable for a wider variety of plants, including:
|
|
|

Why Planta Greenhouses?
- Wind resistant up to 65 mph (learn more about how our greenhouses hold up in high-altitude climates).
- Withstands a snow load of up to 98 psf (480kg/square meter).
- Made with a heavy-duty galvanized steel frame.
- Polycarbonate panels provide 100% protection against UV rays.
- The Sungrow greenhouse is bell-shaped - allows the wind, snow, and hail to slide off the sides.
- Extendable (Sungrow, Sigma and Farmer models can be extended beyond 100ft)
- Made in Europe and are exclusively imported
- Maintenance-free